
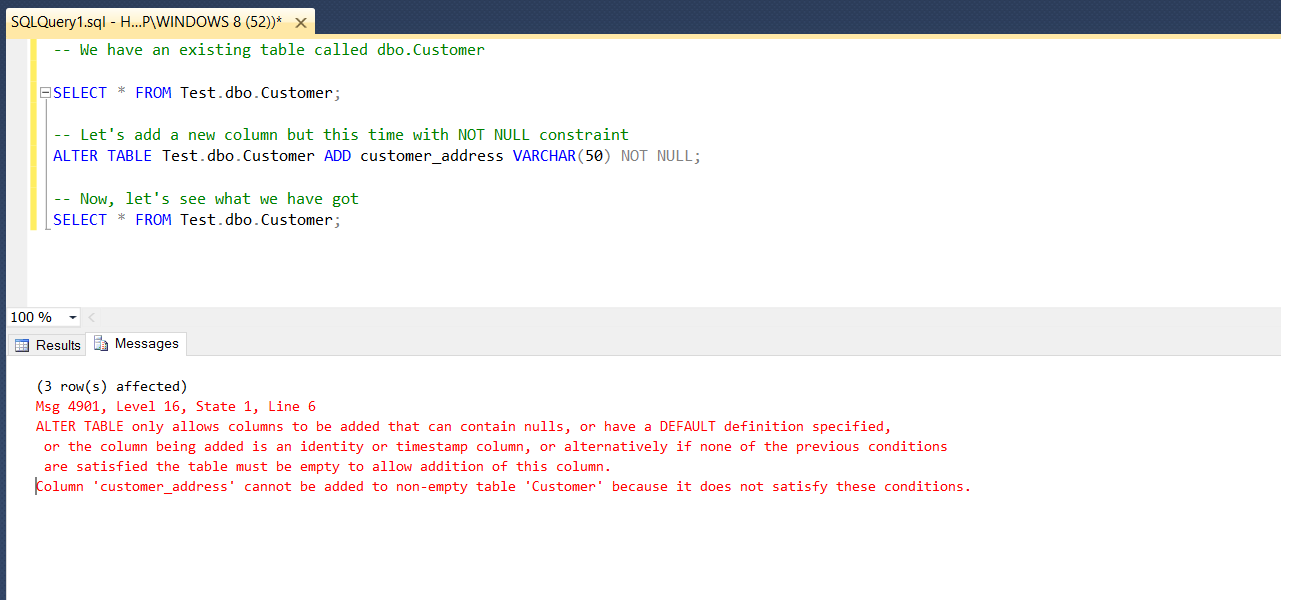
EXTERNAL is for external, uncompressed data, and EXTENDED is for external, compressed data. PLAIN must be used for fixed-length values such as integer and is inline, uncompressed. This controls whether this column is held inline or in a secondary TOAST table, and whether the data should be compressed or not. This form sets the storage mode for a column.
ALTER TABLE ADD COLUMN POSTGRES UPDATE
For more information on the use of statistics by the PostgreSQL query planner, refer to Section 14.2.Ĭhanging per-attribute options acquires a SHARE UPDATE EXCLUSIVE lock.
Specify a value of 0 to revert to estimating the number of distinct values normally. This can be useful when the size of the table changes over time, since the multiplication by the number of rows in the table is not performed until query planning time.
For example, a value of -1 implies that all values in the column are distinct, while a value of -0.5 implies that each value appears twice on the average. When set to a negative value, which must be greater than or equal to -1, ANALYZE will assume that the number of distinct nonnull values in the column is linear in the size of the table the exact count is to be computed by multiplying the estimated table size by the absolute value of the given number. When set to a positive value, ANALYZE will assume that the column contains exactly the specified number of distinct nonnull values.
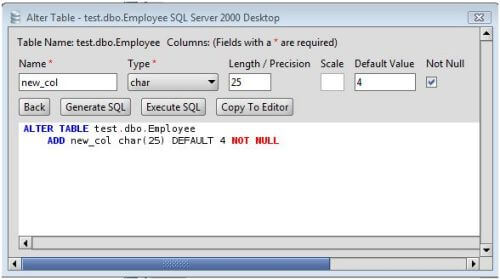
ALTER TABLE ADD COLUMN POSTGRES PLUS
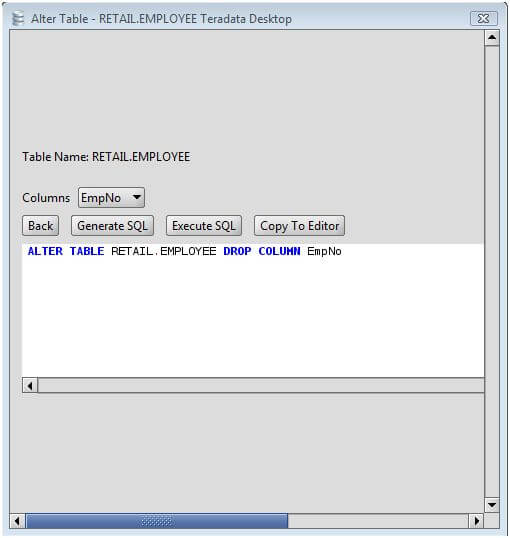
n_distinct affects the statistics for the table itself, while n_distinct_inherited affects the statistics gathered for the table plus its inheritance children. Currently, the only defined per-attribute options are n_distinct and n_distinct_inherited, which override the number-of-distinct-values estimates made by subsequent ANALYZE operations. This form sets or resets per-attribute options. SET STATISTICS acquires a SHARE UPDATE EXCLUSIVE lock. For more information on the use of statistics by the PostgreSQL query planner, refer to Section 14.2. The target can be set in the range 0 to 10000 alternatively, set it to -1 to revert to using the system default statistics target ( default_statistics_target). This form sets the per-column statistics-gathering target for subsequent ANALYZE operations. sequence_option is an option supported by ALTER SEQUENCE such as INCREMENT BY. These forms alter the sequence that underlies an existing identity column. If DROP IDENTITY IF EXISTS is specified and the column is not an identity column, no error is thrown. These forms change whether a column is an identity column or change the generation attribute of an existing identity column. RENAME CONSTRAINT constraint_name TO new_constraint_nameĪLTER TABLE ALL IN TABLESPACE name ]ĪTTACH PARTITION partition_name FOR VALUES partition_bound_specĭETACH PARTITION partition_name where action is one of:ĪDD column_name data_type ]ĭROP column_name ĪLTER column_name TYPE data_type ĪLTER column_name SET DEFAULT expressionĪLTER column_name DROP DEFAULTĪLTER column_name AS IDENTITY Alternatively, you can add constraints later (see below) after you've filled in the new column correctly.Synopsis ALTER TABLE name ĪLTER TABLE name Keep in mind however that the default value must satisfy the given constraints, or the ADD will fail. In fact all the options that can be applied to a column description in CREATE TABLE can be used here. You can also define constraints on the column at the same time, using the usual syntax:ĪLTER TABLE products ADD COLUMN description text CHECK (description '') To avoid a potentially lengthy update operation, particularly if you intend to fill the column with mostly nondefault values anyway, it may be preferable to add the column with no default, insert the correct values using UPDATE, and then add any desired default as described below. However, if the default value is volatile (e.g., clock_timestamp()) each row will need to be updated with the value calculated at the time ALTER TABLE is executed.
Instead, the default value will be returned the next time the row is accessed, and applied when the table is rewritten, making the ALTER TABLE very fast even on large tables. From PostgreSQL 11, adding a column with a constant default value no longer means that each row of the table needs to be updated when the ALTER TABLE statement is executed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
